Mindfulness and emotional exhaustion in call center agents in the Philippines: moderating roles of work and personal characteristics
Call center agents usually experience stress because they need to meet growing customer expectations, unpredictable demands and workloads. These agents may be emotionally troubled because they must cope with challenging customers and at the same time deliver excellent customer service to uphold their organization’s standards. Given the harmful consequences of emotional exhaustion on call center personnel and organizations, it is crucial to understand certain personal characteristics of individuals that might prevent emotional exhaustion at work. One such individual characteristic that has been proposed frequently in research to help employees manage psychological stress in a workplace effectively is “mindfulness”.
In particular, this benefit of mindfulness in the context of call center industry has been unveiled in the research of the ICO NIDA’s faculty member, Associate Professor Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol, which is published in “the Journal of General Psychology” (Scopus/Scimago Q2). The research was coauthored with the ICO NIDA’s alumni, Dr. Jenette Villegas Puyod.
Their research collected survey data from call center agents working at five business process outsourcing units in the Philippines. The results they obtain clearly show that call center agents who possess a higher level of mindfulness tend to experience a lower level of emotional exhaustion. However, their results additionally show that not all groups of call center agents tend to benefit from mindfulness in terms of stress reduction to the same extent. They found that the negative effect of mindfulness on emotional exhaustion of call center agents is particularly strong for (1) those who experience high job demands, (2) those who hold a supervisory position, (3) those who are young, and (4) those who are single. For these four groups of agents, the higher the quality of mindfulness they possess, the lower the level of emotional exhaustion they experience.
In the end, their research recommends that the companies that operate call center business may need to provide mindfulness training for employees to help them develop and/or improve their quality of mindfulness. A mindfulness exercise, such as meditation, could be offered to employees during breaks or before or after work hours to help them relax from work strain. The training should be required particularly for those who hold a supervisory position and those who work in a job function that involves a heavy workload. Moreover, companies may make the training mandatory for young employees and for those who are single. As these two groups tend to be less emotionally mature, mindfulness training might be a more effective intervention that helps reduce the probability that they will experience the emotional exhaustion that can occur easily in their jobs.
Reference
Charoensukmongkol, P., & Puyod, J. V. (2022). Mindfulness and emotional exhaustion in call center agents in the Philippines: Moderating roles of work and personal characteristics, The Journal of General Psychology, 149(1), 72-96. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221309.2020.1800582
- Published in RESEARCH
Benefits of workplace spirituality on real estate agents’ work outcomes: the mediating role of person-Job fit
Mr. Peetikarn Pattanawit, a Ph.D. candidate of ICO NIDA, recently published part of his dissertation in the “Management Research Review”, which is the journal ranked in the “SCImago Quartile 2” and the “Scopus Top 21 percentile”.
The key tenet of his research is about work motivation of real estate agents. Basically, the real estate industry has been characterized as a sector that has a high turnover rate compared to others. Although the opportunity to make substantial commissions appears to tempt people to choose this career, many of them seem to have low intrinsic motivation and do not see the meaning in the tasks that they perform. Due to this problem, his research was conducted to examine what characteristics of the workplace may be able to motivate real estate agents intrinsically and help them develop a sense of meaning in their work.
Theoretically, his research applies the person-environment fit theory to verify the effect of “Workplace spirituality” on real estate agents’ person-job (P-J) fit, customer-oriented organizational citizenship behavior (CO-OCB) and job performance that real estate agents demonstrate. Fundamentally, “Workplace spirituality” represents the characteristics of the work environment that allow employees to discover the meaning in their work, develop strong connections with other organizational members, and establish an alignment between their core beliefs and the organization’s values.
From the analysis of the survey data collected from 398 agents working at 60 brokerage firms in Bangkok, his results showed that real estate agents working in an environment that had a high level of workplace spirituality tended to demonstrate a high level of P-J fit. The greater their P-J fit, the more the CO-OCB and greater the job performance they demonstrated.
In the end, his research offers some recommendations for human resources management in brokerage firms that could help them enhance their agents’ work motivation and performance. The management is recommended to develop and maintain an organizational environment that fosters meaningful work, a sense of community and alignment with organizational values. These practices are expected to help the agents acquire the sense of workplace spirituality, which can enhance their P-J fit subsequently and motivate them intrinsically to be more enthusiastic and more productive in performing their sales tasks.
His research was under close supervision and guidance of his thesis adviser, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol.
Source:
Pattanawit, P., & Charoensukmongkol, P. (2022). Benefits of Workplace Spirituality on Real Estate Agents’ Work Outcomes: The Mediating Role of Person-Job Fit. Management Research Review. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-06-2021-0482
- Published in RESEARCH
How Chinese expatriates’ cultural intelligence promotes supervisor-subordinate Guanxi with Thai Employees: The mediating effect of expatriates’ benevolence
Expatriates assigned by multinational enterprises (MNEs) to manage subsidiaries in foreign countries often play a critical role in determining the MNEs’ global performance. However, cultural differences between the expatriate’s home and host countries can make it difficult for them to work effectively with local employees. Therefore, expatriates must possess cross-cultural competence to increase their effectiveness in working with foreign employees and managing subsidiaries in their host country.
The evidence about this role of cross-cultural competence has been documented in the recent research by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol, which is published in the “Scopus Top 6 percentile journal (Scimago Quartile 1)”. In particular, his research proposes that one characteristic that determines expatriates’ ability to effectively handle international assignments is cultural intelligence (CQ). His research collected survey data from 201 dyads of Chinese expatriates and Thai employees at the subsidiaries of Chinese multinational enterprises in Thailand. His results indicate that CQ facilitates the Chinese expatriates to understand Thai employees’ cultural characteristics and help them make appropriate cultural adaptations accordingly. This could lead the Thai employees to have a favorable attitude toward the Chinese expatriates and view them as benevolent supervisors, thereby encouraging the Thai employees to develop close interpersonal relationship with the Chinese expatriates.
For the recommendation for MNEs, his research suggests that the selection of the expatriates for the international assignment may need to be based on their level of cross-cultural competence. Alternatively, MNEs could offer extensive cross-cultural training to their prospective expatriates. These recommendations can help expatriates develop a strong understanding of the cultures of local employees in the host country, thereby promoting the opportunity to establish a trusting relationship with local employees and enhance their effectiveness in cross-cultural management
Source:
Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021), How Chinese Expatriates’ Cultural Intelligence Promotes Supervisor-Subordinate Guanxi with Thai Employees: The Mediating Effect of Expatriates’ Benevolence, International Journal of Cross Cultural Management, 21(1), 9-30. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470595821996735
- Published in RESEARCH
A Cross-Cultural Perspective on Factors that Influence the Intention to Repurchase in Online Marketplace: A Compairison Between Thailand and Germany
Mr. Bastian Eine, a recent Ph.D. graduate of ICO NIDA from Germany, successfully published part of his dissertation in the “Asian Journal of Business Research”, which is ranked in the “SCImago Quartile 3” (Scopus).
His research examined the effect of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, trust in the sellers, and perceived sellers’ risk on the intention to repurchase in online marketplaces, by performing the cross-country analysis between Thailand and Germany. His online survey data were collected from 404 Thai and 405 German participants. The results showed that the effect of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and trust in the sellers were significantly higher in Thai than in German respondents. However, there was no significant difference between the two nationalities in the effect of perceived sellers’ risk on the intention to repurchase in online marketplaces.
In the end, his research recommended international companies’ managers and cross-cultural marketers to develop different strategies for different countries based on consumers’ cultural characteristics.
His research was under close supervision and guidance of his thesis adviser, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol.
Reference
Eine, B., & Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021). The Cross-Cultural Perspective of Factors Influencing Online Shopping Intention: A Comparison Between Thai and German, Asian Journal of Business Research, 11(1), 20-39. https://doi.org/10.14707/ajbr.210097
- Published in RESEARCH
The Influence of Chinese University Student’ Reinforcement Sensitivity on Cyber Violence
Mr Juntao Zhang, ICO PhD student, recently published his work in Humanities and Social Sciences Letters. His research title is The influence of Chinese University students’ reinforcement sensitivity on cyber violence. His work is under supervision of Dr Zhongwu Li.
- Published in RESEARCH
Leveraging the Power of Online Referral for E-Business: The Moderated Mediation Model
The rise of e-commerce has dramatically changed customer behavior. In the online service sector, a Consumer Review Survey 2020 showed that almost up to 90% of consumers read online referrals (interchangeable with electronic word-of-mouth and online reviews) for relevant information before making a purchase. In other words, when consumers are fairly active in searching for specific types of information while assessing online products and services, they simultaneously search for feedback from other consumers as their key resources in the decision-making process. From this point of view, online referrals would rather serve an indirect role than be a direct variable that significantly influences purchase intention.
This role of online referrals is confirmed in the recent study of the faculty of ICO NIDA, Dr. Chih-Hung Chen. From the analysis of the survey data collected from 418 respondents of an online English company, his research initially shows that four aspects of online service quality (reliability, responsiveness, competence, and engagement) are the significant factors that lead to positive consumer perception and online purchase intention. Moreover, his analysis confirms that online customer referral has a profound effect on consumer perception.
In the end, his research suggests that online referrals seem to play a critical role in purchase intention in the e-commerce market. Online customer referral, therefore, may help e-learning companies to improve service quality with key features that better positions them to target online learners.
Reference
Chen, C.-H. (2021), Leveraging the Power of Online Referral for E-Business: The Moderated Mediation Model. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(7), 2594–2607. https://www.mdpi.com/0718-1876/16/7/143
- Published in RESEARCH
An analysis of impact of personality traits and mindfulness on risk aversion of individual investors
The recent research of the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Vesarach Aumeboonsuke (coauthoring with Prof. Dr. Anetta Caplanova) shows that mindfulness and personalities of investors can affect their risk aversion.
Their research analyses the survey data collected among 100 Thai individual investors. The results show that agreeable people tend to be significantly less mindful, whereas individuals exhibiting conscientiousness, emotional stability and openness tend to be significantly more mindful. Moreover, the analysis of factors affecting risk aversion indicates that people characterized by agreeableness and emotional stability are significantly less risk averse, but people characterized by conscientiousness and openness are significantly more risk averse. Lastly, their research found that older people and women tend to be more risk averse, but men and married individuals have lower degree of risk aversion.
Their research provides more understanding about the role of psychological characteristics and socio-demographic factors that can influence trading behavior of investors. This knowledge might be useful for formulating appropriate regulatory practices (for example, by using behavioral nudges aimed to improve investment outcomes of individual investors and to mitigate undesirable divergence of investment behavior of individual investors from rationality).
Reference:
Aumeboonsuke, V., Caplanova, A. (2021). An analysis of impact of personality traits and mindfulness on risk aversion of individual investors. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02015-9
- Published in RESEARCH
Interacting Effect of Social Media Crisis Communication and Organizational Citizenship Behavior on Employees’ Resistance to Change during the COVID-19 Crisis: Evidence from University Employees in the Philippines
The recent research conducted by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol (coauthoring with Dr. Jenette Villegas Puyod), provided interesting evidence about the management practice to prevent employees’ resistance to change during this COVID-19 crisis.
Basically, resistance to change is a common phenomenon that happens among employees during the period of organizational change and transformation. Particularly amid the period of transformation caused by the COVID-19 crisis, employees’ resistance to change can be deleterious to the vitality of the organization to get through the crisis situation.
Under this uncertain circumstance, their research suggests that communication from management provided through the social media channel of the organization seems to be the effective practice to prevent and lessen employees’ resistance to change and their negative reactions during an organizational crisis. Basically, when employees obtain sufficient information conveyed by the management, they can have a clear understanding about the difficulties the organization is facing and the underlying reasons for the changes that need to be done to deal with the crisis.
However, their research noted that even when the crisis communication is effectively delivered to employees, employees may still feel reluctant to support the change when they do not gain sufficient support from their colleagues. For this reason, the altruistic behavior of employees in terms of Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) is required to enhance the effect of communication on lessening employees’ resistance to change. Basically, OCB is the willingness of employees to voluntarily contribute to the organization beyond the scope of their responsibilities. The beneficial role of OCB during the change period is to promote helping behaviors and collaboration among employees, which facilitate them to collectively embrace the change initiative communicated by management.
Based on the survey data they collected from 522 employees from three public universities in the Philippines, they found that crisis communication could have a stronger impact on lowering employees’ resistance to change when OCB was highly expressed among employees. This finding implies that the crisis communication from management alone may not be sufficient to reduce employees’ resistance to change without interacting with OCB from employees.
In conclusion, their research recommended the management to quickly communicate information efficiently and effectively to employees during the crisis to ensure their employees have clear knowledge of the situation and to avoid negative reactions from employees. Apart from its role in crisis communication, it is equally important for management to encourage its employees to support each other and the organization by engaging in OCB. In this regard, the communication from management during the crisis must also contain a message that inspires employees to realize the importance of OCB as an imperative practice to help organization members and the organization itself collectively and successfully get though the crisis.
Source:
Puyod, J. V., & Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021), Interacting Effect of Social Media Crisis Communication and Organizational Citizenship Behavior on Employees’ Resistance to Change during the COVID-19 Crisis: Evidence from University Employees in the Philippines, Asia-Pacific Social Science Review, 21(3), 13–27.
- Published in RESEARCH
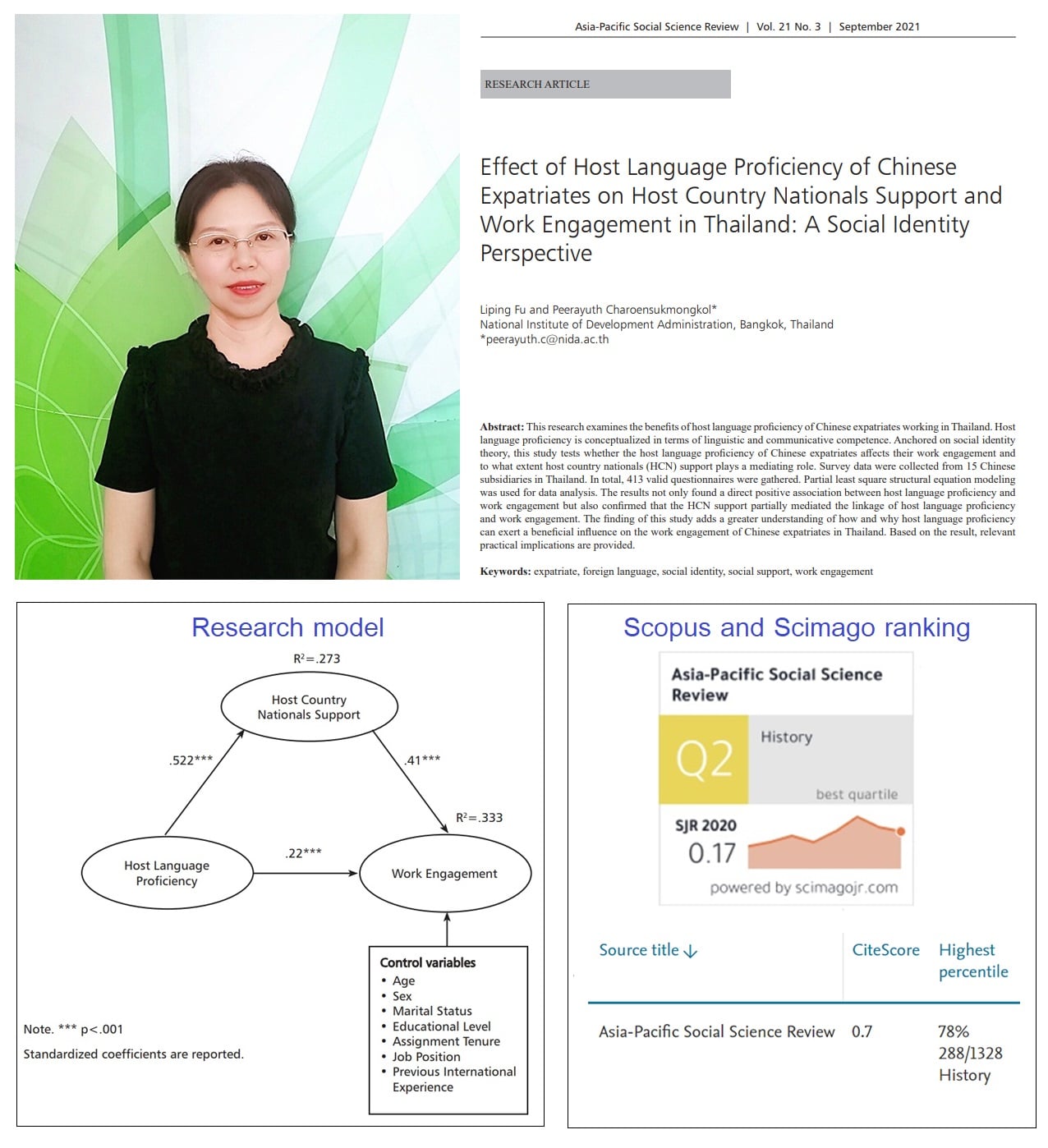
Effect of Host Language Proficiency of Chinese Expatriates on Host Country Nationals Support and Work Engagement in Thailand: A Social Identity Perspective.
Ms. Liping Fu (Maria), a recent Ph.D. graduate of ICO NIDA, published the “second paper” from her dissertation. This paper is published in the “Asia-Pacific Social Science Review”, which is ranked in the “SCImago Quartile 2” and “Scopus top 22 percentile”.
Her research applies the “Social identify theory” to explain the essential role of host language proficiency in helping the Chinese expatriate working in Thailand to obtain more social support from Thai coworkers and to improve their work engagement.
From the analysis of survey data collected from 413 Chinese expatriates in 15 subsidiaries in Thailand, her study found that Chinese expatriates who were proficient in Thai communication could establish close relationships with Thai coworkers. The social support delivered by Thai coworkers subsequently helped expatriates to engage effectively in their international assignments.
Based on the findings, her study recommends that MNEs should pay special attention to host language proficiency, rather than ignoring it and adopting the assumption that English has become the common language in the world. Therefore, host language proficiency should be considered as a linguistic strategy when MNEs plan to localize their business operations in a particular foreign country.
Her research was under close supervision and guidance of her thesis adviser, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol.
Reference: Fu, L., & Charoensukmongkol, P., & (2021), Effect of Host Language Proficiency of Chinese Expatriates on Host Country Nationals Support and Work Engagement in Thailand: A Social Identity Perspective, Asia-Pacific Social Science Review, 21(3), 180 – 195.
The paper can be downloaded from http://apssr.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/RA-13.pdf
- Published in RESEARCH
Influence of Transformational Leadership on Role Ambiguity and Work-Life Balance of Filipino University Employees During COVID-19: Does Employee Involvement Matter?
One particular impact that employees inevitably experience when they have to work from home (WFH) during the COVID-19 pandemic is the lack of “Work–Life Balance”. Basically, when people work at home, they tend to dedicate more time into working and simply lose track of time due to the lack of boundary between work and home. One possible reason that creates lack of Work–Life Balance is the role ambiguity problem that employees experienced when they WFH. In particular, role ambiguity seems to be a common problem for WFH employees because moving to teleworking from home lead to unclear information, instructions, and expectations regarding the tasks that employees need to perform. This situation tends to make employees to experience confusion regarding how to perform effectively with increasing workloads, which can potentially lead them to suffer from lack Work–Life Balance as a result.
The evidence about the role ambiguity problem and the lack of Work–Life Balance during the COVID19 pandemic has been documented in the recent research conducted by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol (coauthoring with Dr. Jenette Villegas Puyod), which is published in the International Journal of Leadership in Education (Scimago Quartile 1).
Their study, which collected data from employees at three public universities in the Philippines, found some evidence regarding the negative effect of role ambiguity that university employees experienced when they WFH during the COVID-19 pandemic. The role ambiguity problem was found as a key factor that created lack of work–life balance among the employees. However, their study also found that employees who worked for the supervisor possessing transformational leadership characteristics tended to experience less role ambiguity and tended to show higher work–life balance. However, their research additionally indicates that the management policy that involved employee to take part in decision making was not recommended during the WFH period, as it tended to create excessive burden that increased role ambiguity of the employees.
In the end, their study suggested that transformational leadership behaviors of people who take a managerial role in the workplace are required during the crisis to help employees have a clear understanding of how to deal with uncertainty in their work roles and responsibilities. In particular, this type of leaders will be able to provide assistance and support to help employees have clear understandings about how to deal with issues from the crisis, thereby facilitating the employees to maintain a good work–life balance as a result.
Reference:
Charoensukmongkol, P., & Puyod, J. V. (2021), Influence of Transformational Leadership on Role Ambiguity and Work-Life Balance of Filipino University Employees During COVID-19: Does Employee Involvement Matter?, International Journal of Leadership in Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/13603124.2021.1882701
- Published in RESEARCH
Promoting Information-Resource Sharing within the Enterprise: A Perspective of Blockchain Consensus Perception
Mr. Gang Li, a recent Ph.D. graduate of ICO NIDA, published his dissertation in the “Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity”, which is ranked in the “SCImago Quartile 2”. His work is under supervision of Dr. Chih-Cheng Fang (Francis).
- Published in RESEARCH
Effects of workplace rumors and organizational formalization during the COVID-19 pandemic: a case study of universities in the Philippines
During the organizational crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, rumors that spread in the workplace seem to have considerable effects on employees’ psychological well-being by aggravating panic and fear. Rumors also confuse employees and lead to distress. They ultimately produce a poor working environment and reduce work productivity.
The research evidence about the negative impacts of workplace rumors during the COVID-19 pandemic is recently documented in the study conducted by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol, and his colleague, Dr. Jenette Villegas Puyod, which is published in the International Journal of Corporate Communications (Scimago Quartile 2)
From the analysis of the online survey data obtained from 522 faculty members and staff at three public universities in the Philippines, their research shows that employees who were exposed frequently to workplace rumors were likely to feel more ambiguous about their work role and be more emotionally exhausted during the pandemic. Their research additionally found that employees in the highly formalized workplace who were also exposed to more workplace rumors tended to be those who experienced the greatest degrees of role ambiguity and emotional exhaustion.
In the conclusion, their study suggests that management should be concerned about the negative side of rumors that could potentially create more uncertainty and ambiguity during such times. Because rumors normally abound in an organization when official communication is not managed effectively, it is imperative for management to communicate to employees constantly and clearly to ease their concern and uncertainty related to the extra roles they must undertake during a crisis.
Reference
Puyod, J. V., & Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021), Effects of Workplace Rumors and Organizational Formalization During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of Universities in the Philippines, Corporate Communications: an International Journal. https://doi.org/10.1108/CCIJ-09-2020-0127
- Published in RESEARCH