An analysis of impact of personality traits and mindfulness on risk aversion of individual investors
The recent research of the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Vesarach Aumeboonsuke (coauthoring with Prof. Dr. Anetta Caplanova) shows that mindfulness and personalities of investors can affect their risk aversion.
Their research analyses the survey data collected among 100 Thai individual investors. The results show that agreeable people tend to be significantly less mindful, whereas individuals exhibiting conscientiousness, emotional stability and openness tend to be significantly more mindful. Moreover, the analysis of factors affecting risk aversion indicates that people characterized by agreeableness and emotional stability are significantly less risk averse, but people characterized by conscientiousness and openness are significantly more risk averse. Lastly, their research found that older people and women tend to be more risk averse, but men and married individuals have lower degree of risk aversion.
Their research provides more understanding about the role of psychological characteristics and socio-demographic factors that can influence trading behavior of investors. This knowledge might be useful for formulating appropriate regulatory practices (for example, by using behavioral nudges aimed to improve investment outcomes of individual investors and to mitigate undesirable divergence of investment behavior of individual investors from rationality).
Reference:
Aumeboonsuke, V., Caplanova, A. (2021). An analysis of impact of personality traits and mindfulness on risk aversion of individual investors. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02015-9
- Published in RESEARCH
Interacting Effect of Social Media Crisis Communication and Organizational Citizenship Behavior on Employees’ Resistance to Change during the COVID-19 Crisis: Evidence from University Employees in the Philippines
The recent research conducted by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol (coauthoring with Dr. Jenette Villegas Puyod), provided interesting evidence about the management practice to prevent employees’ resistance to change during this COVID-19 crisis.
Basically, resistance to change is a common phenomenon that happens among employees during the period of organizational change and transformation. Particularly amid the period of transformation caused by the COVID-19 crisis, employees’ resistance to change can be deleterious to the vitality of the organization to get through the crisis situation.
Under this uncertain circumstance, their research suggests that communication from management provided through the social media channel of the organization seems to be the effective practice to prevent and lessen employees’ resistance to change and their negative reactions during an organizational crisis. Basically, when employees obtain sufficient information conveyed by the management, they can have a clear understanding about the difficulties the organization is facing and the underlying reasons for the changes that need to be done to deal with the crisis.
However, their research noted that even when the crisis communication is effectively delivered to employees, employees may still feel reluctant to support the change when they do not gain sufficient support from their colleagues. For this reason, the altruistic behavior of employees in terms of Organizational Citizenship Behavior (OCB) is required to enhance the effect of communication on lessening employees’ resistance to change. Basically, OCB is the willingness of employees to voluntarily contribute to the organization beyond the scope of their responsibilities. The beneficial role of OCB during the change period is to promote helping behaviors and collaboration among employees, which facilitate them to collectively embrace the change initiative communicated by management.
Based on the survey data they collected from 522 employees from three public universities in the Philippines, they found that crisis communication could have a stronger impact on lowering employees’ resistance to change when OCB was highly expressed among employees. This finding implies that the crisis communication from management alone may not be sufficient to reduce employees’ resistance to change without interacting with OCB from employees.
In conclusion, their research recommended the management to quickly communicate information efficiently and effectively to employees during the crisis to ensure their employees have clear knowledge of the situation and to avoid negative reactions from employees. Apart from its role in crisis communication, it is equally important for management to encourage its employees to support each other and the organization by engaging in OCB. In this regard, the communication from management during the crisis must also contain a message that inspires employees to realize the importance of OCB as an imperative practice to help organization members and the organization itself collectively and successfully get though the crisis.
Source:
Puyod, J. V., & Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021), Interacting Effect of Social Media Crisis Communication and Organizational Citizenship Behavior on Employees’ Resistance to Change during the COVID-19 Crisis: Evidence from University Employees in the Philippines, Asia-Pacific Social Science Review, 21(3), 13–27.
- Published in RESEARCH
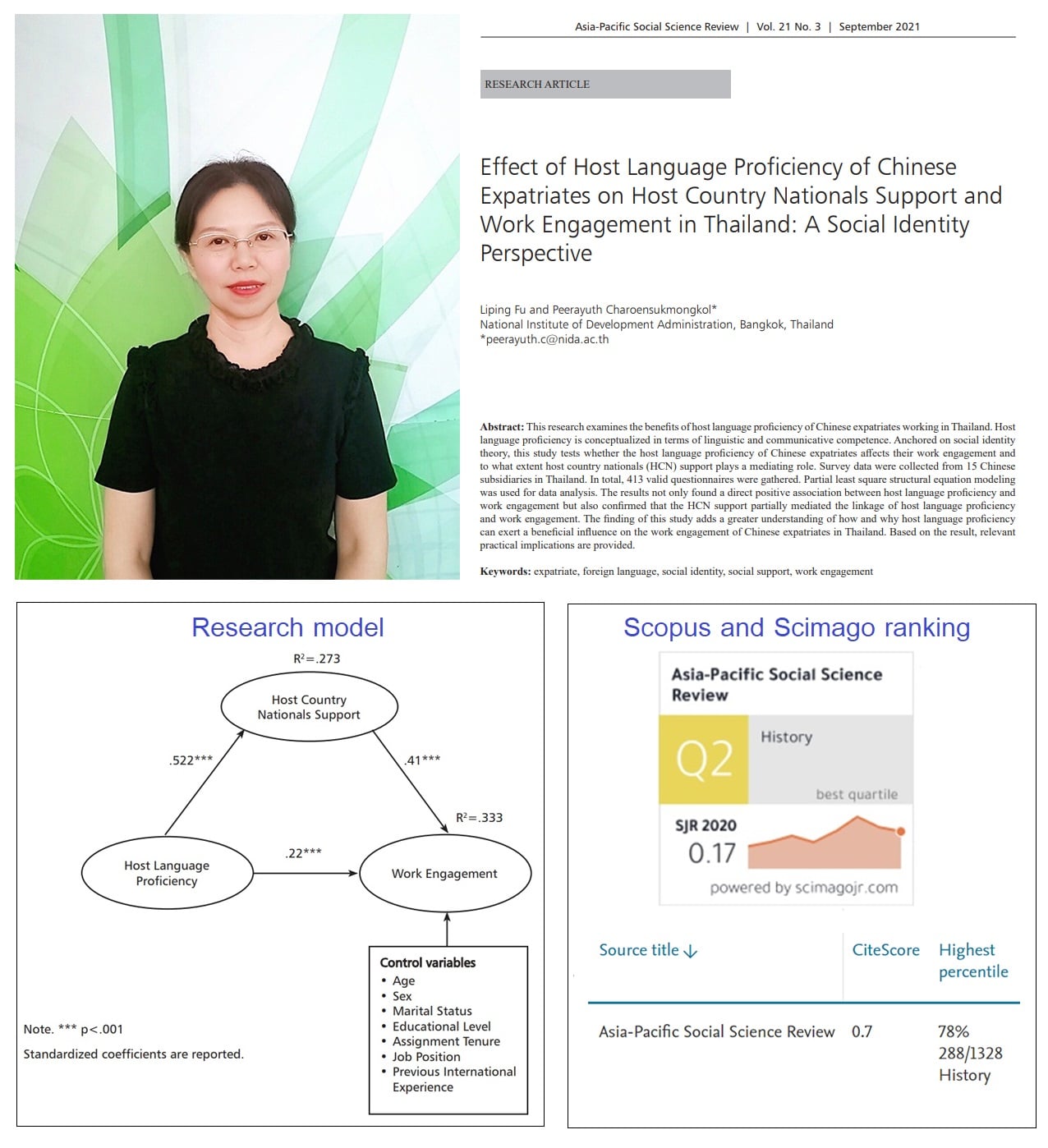
Effect of Host Language Proficiency of Chinese Expatriates on Host Country Nationals Support and Work Engagement in Thailand: A Social Identity Perspective.
Ms. Liping Fu (Maria), a recent Ph.D. graduate of ICO NIDA, published the “second paper” from her dissertation. This paper is published in the “Asia-Pacific Social Science Review”, which is ranked in the “SCImago Quartile 2” and “Scopus top 22 percentile”.
Her research applies the “Social identify theory” to explain the essential role of host language proficiency in helping the Chinese expatriate working in Thailand to obtain more social support from Thai coworkers and to improve their work engagement.
From the analysis of survey data collected from 413 Chinese expatriates in 15 subsidiaries in Thailand, her study found that Chinese expatriates who were proficient in Thai communication could establish close relationships with Thai coworkers. The social support delivered by Thai coworkers subsequently helped expatriates to engage effectively in their international assignments.
Based on the findings, her study recommends that MNEs should pay special attention to host language proficiency, rather than ignoring it and adopting the assumption that English has become the common language in the world. Therefore, host language proficiency should be considered as a linguistic strategy when MNEs plan to localize their business operations in a particular foreign country.
Her research was under close supervision and guidance of her thesis adviser, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol.
Reference: Fu, L., & Charoensukmongkol, P., & (2021), Effect of Host Language Proficiency of Chinese Expatriates on Host Country Nationals Support and Work Engagement in Thailand: A Social Identity Perspective, Asia-Pacific Social Science Review, 21(3), 180 – 195.
The paper can be downloaded from http://apssr.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/RA-13.pdf
- Published in RESEARCH
Influence of Transformational Leadership on Role Ambiguity and Work-Life Balance of Filipino University Employees During COVID-19: Does Employee Involvement Matter?
One particular impact that employees inevitably experience when they have to work from home (WFH) during the COVID-19 pandemic is the lack of “Work–Life Balance”. Basically, when people work at home, they tend to dedicate more time into working and simply lose track of time due to the lack of boundary between work and home. One possible reason that creates lack of Work–Life Balance is the role ambiguity problem that employees experienced when they WFH. In particular, role ambiguity seems to be a common problem for WFH employees because moving to teleworking from home lead to unclear information, instructions, and expectations regarding the tasks that employees need to perform. This situation tends to make employees to experience confusion regarding how to perform effectively with increasing workloads, which can potentially lead them to suffer from lack Work–Life Balance as a result.
The evidence about the role ambiguity problem and the lack of Work–Life Balance during the COVID19 pandemic has been documented in the recent research conducted by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol (coauthoring with Dr. Jenette Villegas Puyod), which is published in the International Journal of Leadership in Education (Scimago Quartile 1).
Their study, which collected data from employees at three public universities in the Philippines, found some evidence regarding the negative effect of role ambiguity that university employees experienced when they WFH during the COVID-19 pandemic. The role ambiguity problem was found as a key factor that created lack of work–life balance among the employees. However, their study also found that employees who worked for the supervisor possessing transformational leadership characteristics tended to experience less role ambiguity and tended to show higher work–life balance. However, their research additionally indicates that the management policy that involved employee to take part in decision making was not recommended during the WFH period, as it tended to create excessive burden that increased role ambiguity of the employees.
In the end, their study suggested that transformational leadership behaviors of people who take a managerial role in the workplace are required during the crisis to help employees have a clear understanding of how to deal with uncertainty in their work roles and responsibilities. In particular, this type of leaders will be able to provide assistance and support to help employees have clear understandings about how to deal with issues from the crisis, thereby facilitating the employees to maintain a good work–life balance as a result.
Reference:
Charoensukmongkol, P., & Puyod, J. V. (2021), Influence of Transformational Leadership on Role Ambiguity and Work-Life Balance of Filipino University Employees During COVID-19: Does Employee Involvement Matter?, International Journal of Leadership in Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/13603124.2021.1882701
- Published in RESEARCH
Promoting Information-Resource Sharing within the Enterprise: A Perspective of Blockchain Consensus Perception
Mr. Gang Li, a recent Ph.D. graduate of ICO NIDA, published his dissertation in the “Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity”, which is ranked in the “SCImago Quartile 2”. His work is under supervision of Dr. Chih-Cheng Fang (Francis).
- Published in RESEARCH
Effects of workplace rumors and organizational formalization during the COVID-19 pandemic: a case study of universities in the Philippines
During the organizational crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, rumors that spread in the workplace seem to have considerable effects on employees’ psychological well-being by aggravating panic and fear. Rumors also confuse employees and lead to distress. They ultimately produce a poor working environment and reduce work productivity.
The research evidence about the negative impacts of workplace rumors during the COVID-19 pandemic is recently documented in the study conducted by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol, and his colleague, Dr. Jenette Villegas Puyod, which is published in the International Journal of Corporate Communications (Scimago Quartile 2)
From the analysis of the online survey data obtained from 522 faculty members and staff at three public universities in the Philippines, their research shows that employees who were exposed frequently to workplace rumors were likely to feel more ambiguous about their work role and be more emotionally exhausted during the pandemic. Their research additionally found that employees in the highly formalized workplace who were also exposed to more workplace rumors tended to be those who experienced the greatest degrees of role ambiguity and emotional exhaustion.
In the conclusion, their study suggests that management should be concerned about the negative side of rumors that could potentially create more uncertainty and ambiguity during such times. Because rumors normally abound in an organization when official communication is not managed effectively, it is imperative for management to communicate to employees constantly and clearly to ease their concern and uncertainty related to the extra roles they must undertake during a crisis.
Reference
Puyod, J. V., & Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021), Effects of Workplace Rumors and Organizational Formalization During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of Universities in the Philippines, Corporate Communications: an International Journal. https://doi.org/10.1108/CCIJ-09-2020-0127
- Published in RESEARCH
Does entrepreneurs’ improvisational behavior improve firm performance in time of crisis?
The recent research published by the faculty of ICO NIDA, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Peerayuth Charoensukmongkol, indicates that one crucial characteristic of entrepreneurs that could contribute to the survival of SMEs during the economic crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic is “Improvisational behavior”.
Improvisational behavior is a spontaneous action guided by intuition, produced or carried out in the spur of the moment instead of going through intentional thought and evaluation processes. Basically, individuals who possess improvisational behavior can be described by three main characteristics. First, they have the ability to perform tasks effectively under time pressure. Second, they tend to be innovative in how to combine and use resources at hand toward new problems and opportunities. Third, they generally have perseverance and do not give up easily when experiencing setbacks and failure.
Improvisational behavior is particularly imperative during the crisis when entrepreneurs have little time, expertise, or inclination for contingency planning. Because the unpredictable economic impacts resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted virtually every aspect of business activities, entrepreneurs who rigidly depend on preplanned routines and decision-making could suffer from the inability to respond quickly to the disruption brought on by the crisis. With improvisational behavior, entrepreneurs can make decisions on the spot to solve unexpected problems, thereby enhancing the proactiveness of their business to deal with contingencies caused by the pandemic. It also gives them more flexibility to make adjustments and be more responsive to a changing and uncertain business environment during the economic crisis.
The results from his research, which collected data from the sample of 312 SMEs during the second wave of COVID-19 pandemic in Thailand, supports the positive relationship between the improvisational behavior of entrepreneurs and firm performance. Moreover, the positive impact of improvisational behavior on firm performance tends to be stronger for firms that encountered a higher level of competitive intensity and for firms that possessed a higher level of financial and human resources.
His research provides important recommendations regarding the competency development of entrepreneurs that are required to enable them to manage their business successfully during the economic crisis. Considering the disruptive nature and the unpredictability of the COVID-19 pandemic which constrained the ability of entrepreneurs to rely on formalized strategic decision-making or long-term strategic planning to deal with the volatility of the business environment, improvisation is recommended as the competency that entrepreneurs need to develop to enhance their capability to deal with contingencies that arise during the crisis.
Source:
Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021), Does Entrepreneurs’ Improvisational Behavior Improve Firm Performance in Time of Crisis?, Management Research Review. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-12-2020-0738
- Published in RESEARCH
Psychological contract, organizational commitment, and knowledge innovation: A perspective of open innovation
Ms. Ling Peng, a recent Ph.D. graduate of ICO NIDA, published her dissertation in the Scopus database journal “Problems and Perspectives in Management”. Her work is under supervision of Dr. ZhongWu Li. More detail of the paper can be found via https://www.businessperspectives.org/index.php/journals/problems-and-perspectives-in-management/issue-380/psychological-contract-organizational-commitment-and-knowledge-innovation-a-perspective-of-open-innovation?fbclid=IwAR1r0lONxvK5XKVtrlu_J0iwiS1KXxyJkWU-B04z2_TORI6lSR048x9lNj8
- Published in RESEARCH
Big Data Development of Tourism Resources Based on 5G Network and Internet of Things System
Mr. Haifeng Gao has recently published his dissertation in the “Microprocessors and Microsystems”, which is ranked in the “SCImago Quartile 3”. His work is under supervision of Dr. ZhongWu Li.
- Published in RESEARCH
Employee Characteristics, Subjective Norms and Work Performance: Integrating the Achievement Goal Orientation Theory and the Theory of Planned Behavior
- Published in RESEARCH
National Institute of Development (NIDA) Student Invitation for Free COVID-19 Vaccination
- Published in NEWS
Effect of cultural intelligence on burnout of Chinese expatriates in Thailand: The mediating role of host country national coworker support
Fu, L., & Charoensukmongkol, P. (2021), Effect of cultural intelligence on burnout of Chinese expatriates in Thailand: The mediating role of host country national coworker support. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/
- Published in RESEARCH